Coqui Francolin
Posted: Mon May 21, 2012 7:11 pm
188. Coqui Francolin Peliperdix coqui (Swempie)
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
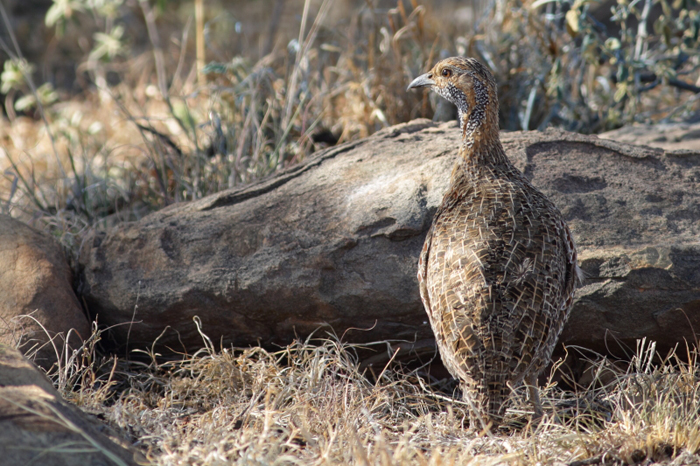
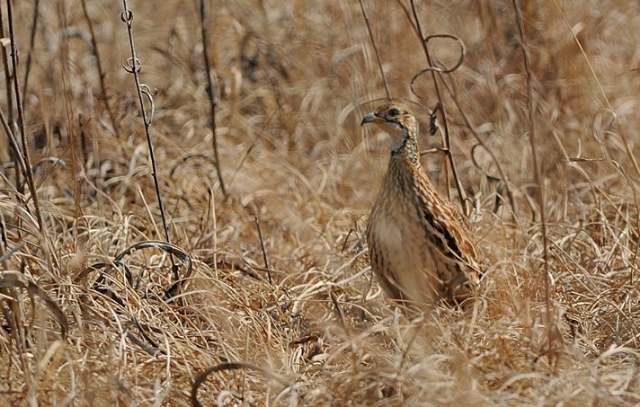
Length 20-28 cm, weight 191-314 g. The Coqui Francolin is arguably the smallest francolins in southern Africa. Bill black with yellow base. Legs yellow.
The adult male is easily distinguished from other francolins by the plane reddish-brown head contrasting with the barred underparts. Ad male: Head plain mustard yellow, crown dark chestnut. Lower neck, mantle and upper breast densely barred black and white. Remainder of upper parts mostly brown, feathers with white to buff central streak and buff transverse barring, together forming criss-cross pattern; some irregularly blotched black. Tail orange-buff, conspicuous in flight but at rest largely obscured by long, barred upper tail coverts. Lower breast and belly pale cream, barred black, bars forming series of chevrons. Bill grey with yellow base. Eyes reddish brown. Legs rich yellow, with moderate tarsal spurs.
Adult female: Has a pale eyebrow with black stripe above and white throat with black border and plain buffy breast.
Juvenile resembles female, but less streaked above.
Similar species: The female can be distinguished from other francolins, Shelley's Francolin in particular, by the white eye stripe and lack of chestnut stripes on breast and flanks.
Distribution
Sub-Saharan Africa: Senegal and southern Ethiopia to north-eastern South Africa.
Habitat
Woodland and savanna; especially those with sandy soils.
Diet
Feeds mainly on above ground food such as seeds, shoots and small fruits. To a lesser extent feeds on underground corms and bulbs, using mainly its bill rather than scratching the soil with its legs as in most other francolins. In the warmer months also feeds in invertebrates.
Breeding
Monogamous. Breeds towards the end of the rainy season or early in the dry season when grass is long and unburnt and seed supply is hence at a peak. Egg-laying season is almost year-round, peaking from December-May. Lays clutch of 3-6 whitish eggs, incubation period unknown, only the female incubates the eggs. The chick can fly after 7-10 days.
Call
High pitched 2-syllable co-qui, co-qui. Dominant call by male is ter, ink, ink, terra, terra, terra. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident. Widespread but with patchy distribution and locally common only in isolated areas.
Order: Galliformes. Family: Phasianidae
Description
Length 20-28 cm, weight 191-314 g. The Coqui Francolin is arguably the smallest francolins in southern Africa. Bill black with yellow base. Legs yellow.
The adult male is easily distinguished from other francolins by the plane reddish-brown head contrasting with the barred underparts. Ad male: Head plain mustard yellow, crown dark chestnut. Lower neck, mantle and upper breast densely barred black and white. Remainder of upper parts mostly brown, feathers with white to buff central streak and buff transverse barring, together forming criss-cross pattern; some irregularly blotched black. Tail orange-buff, conspicuous in flight but at rest largely obscured by long, barred upper tail coverts. Lower breast and belly pale cream, barred black, bars forming series of chevrons. Bill grey with yellow base. Eyes reddish brown. Legs rich yellow, with moderate tarsal spurs.
Adult female: Has a pale eyebrow with black stripe above and white throat with black border and plain buffy breast.
Juvenile resembles female, but less streaked above.
Similar species: The female can be distinguished from other francolins, Shelley's Francolin in particular, by the white eye stripe and lack of chestnut stripes on breast and flanks.
Distribution
Sub-Saharan Africa: Senegal and southern Ethiopia to north-eastern South Africa.
Habitat
Woodland and savanna; especially those with sandy soils.
Diet
Feeds mainly on above ground food such as seeds, shoots and small fruits. To a lesser extent feeds on underground corms and bulbs, using mainly its bill rather than scratching the soil with its legs as in most other francolins. In the warmer months also feeds in invertebrates.
Breeding
Monogamous. Breeds towards the end of the rainy season or early in the dry season when grass is long and unburnt and seed supply is hence at a peak. Egg-laying season is almost year-round, peaking from December-May. Lays clutch of 3-6 whitish eggs, incubation period unknown, only the female incubates the eggs. The chick can fly after 7-10 days.
Call
High pitched 2-syllable co-qui, co-qui. Dominant call by male is ter, ink, ink, terra, terra, terra. Listen to Bird Call.
Status
Common resident. Widespread but with patchy distribution and locally common only in isolated areas.
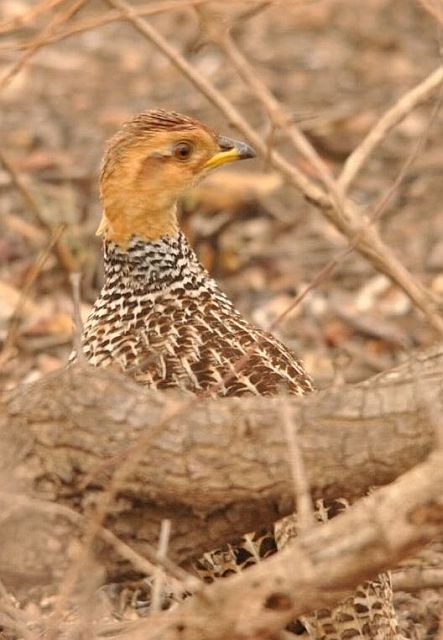 © lowveldboy
© lowveldboy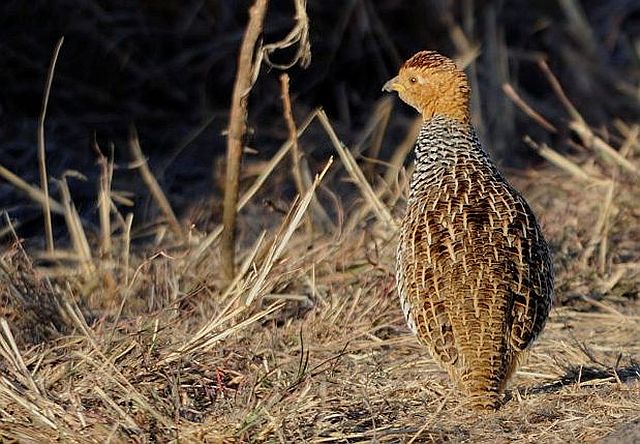 © Dewi
© Dewi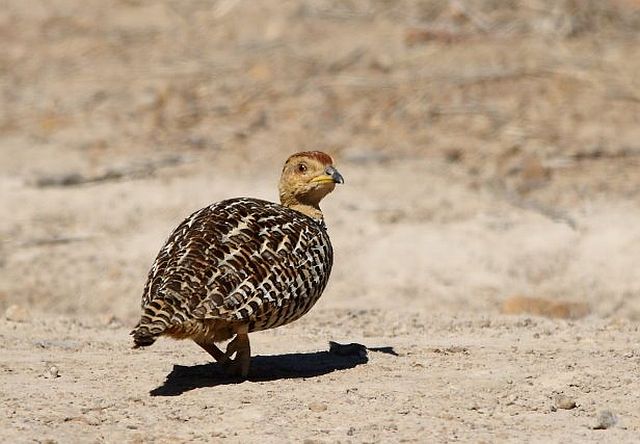 © Flutterby
© Flutterby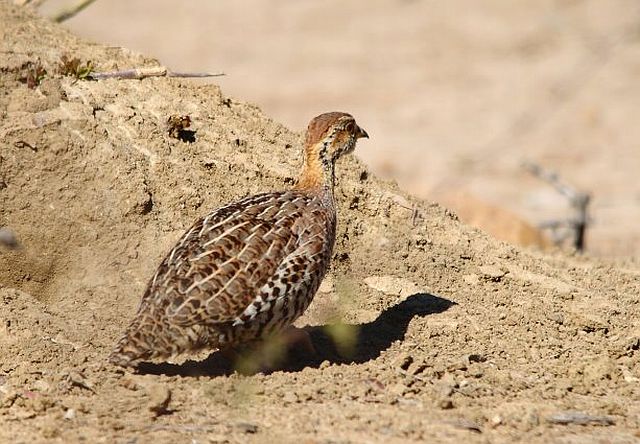 © Flutterby
© Flutterby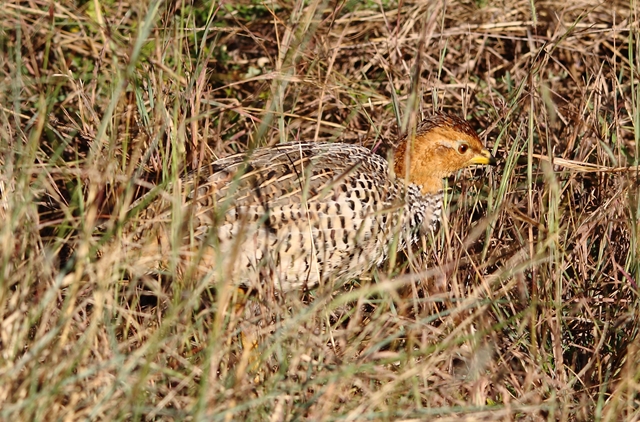 © Flutterby
© Flutterby
 © Puff Addy
© Puff Addy
 © Dewi
© Dewi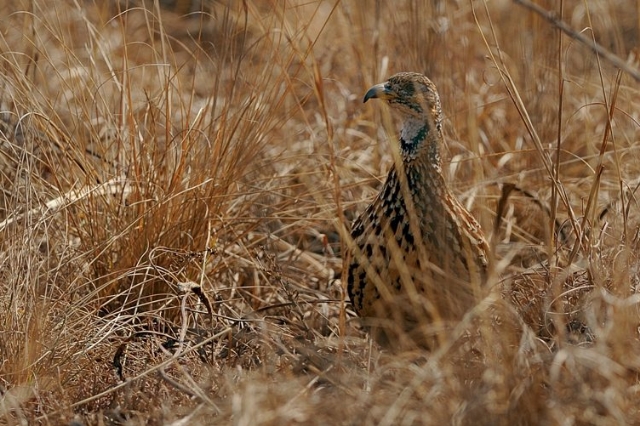 © Dewi
© Dewi © BluTuna
© BluTuna © BluTuna
© BluTuna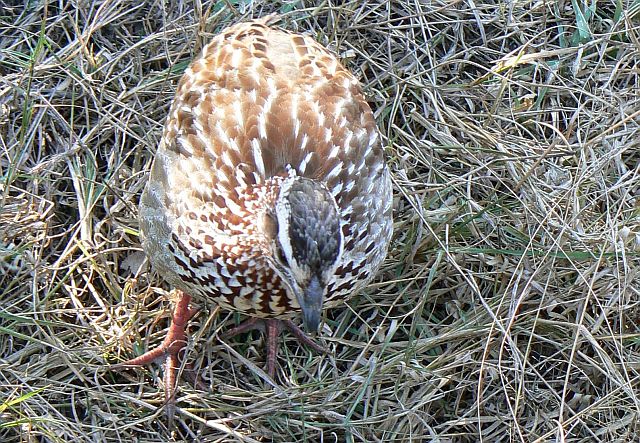 © Toko
© Toko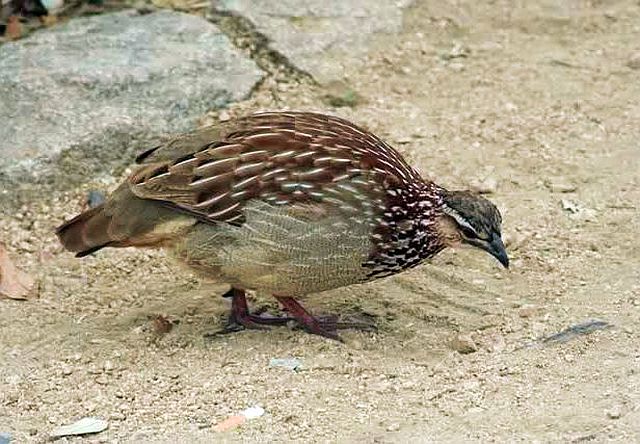 © pooky
© pooky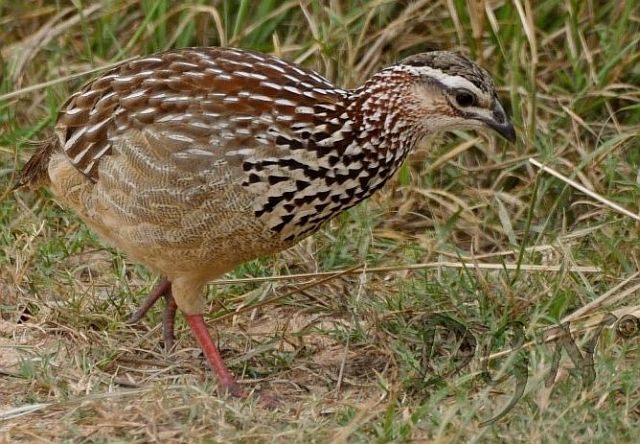 © JustN@ture
© JustN@ture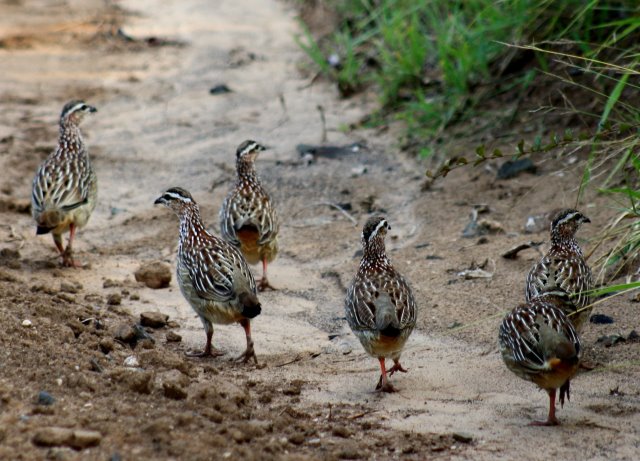 © Flutterby
© Flutterby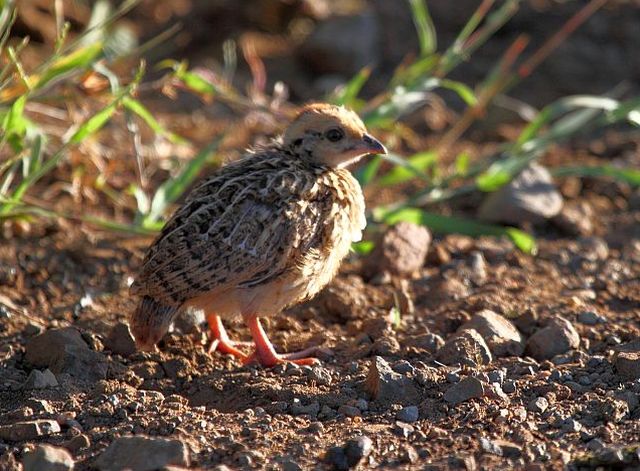 © Duke
© Duke